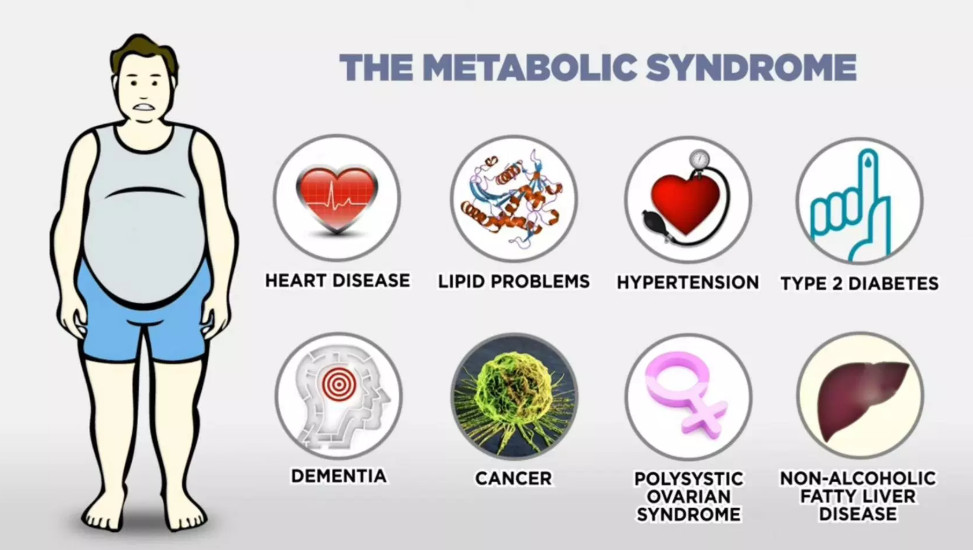
Metabolic disorders are increasingly contributing to the global healthcare burden. The increased prevalence of metabolic disorders has been associated with several factors including change in the environment and lifestyle of individuals. Genetics also contribute to a lot of metabolic disorders. This article focuses on the most common metabolic disorders, also explaining why metabolic disorders occur.
Several processes occur simultaneously to ensure proper functioning of the human body. These metabolic processes which include building up and breaking down of biochemical substances must occur at certain rates and in certain conditions. Metabolic disorders prevent these processes from occurring as they should.
Metabolic disorders can occur across different systems and organs and in different forms. Ultimately, they lead to abnormal body functioning, whether because of a missing or nonfunctional enzyme or because of mutation that cause the form of a biochemical substance.
Some of the most common metabolic disorders are highlighted below.
Diabetes
Diabetes occurs as a result of improper functioning of the glucose metabolism system. Glucose is the form to which most of the food absorbed are converted. Thus, it is product of food taken that the body cells can access.
The types of diabetes result in an ability of the body cells to take up glucose, a processed which is mediated by insulin. Type 1 diabetes results from a congenital lack of insulin and persons suffering from diabetes type 1 need exogenous insulin. Type 2 diabetes occurs as a result of the insensitivity of the body to the insulin it produces.
The higher prevalence of diabetes has been linked to lifestyle changes, especially the type 2 diabetes. Research has shown that about 10% of the American population has diabetes.
Phenylketonuria
Phenylketonuria is a metabolic disorder that is related to protein. Proteins are made up of amino acid, and phenylketonuria occurs as a result of improper metabolism of phenylalanine, an essential amino acid. The pathway of metabolism of phenylalanine involves the initial conversion to tyrosine. The enzyme for this converts ion is phenylalanine hydroxylase. A deficiency of this hormone or the presence of a nonfunctional form of this hormone results in phenylketonuria. Phenylketonuria comes with different symptoms which include organ damage and mental retardation as a result of excess phenylalanine in the body.
Gaucher’s disease
This is another metabolic disorder that occurs as a result of the absence of an enzyme or the presence of an unfunctional form of the enzyme. Gaucher’s disease is as a result of an ability to break down a specific type of fat which causes fat accumulation in organs such as the spleen and liver. Gaucher’s disease comes with several manifestations such as bone damage and could lead to death.
Glucose-galactose malabsorption
This metabolic disorder results from a defect in the glucose and galactose absorption system and can lead to severe diarrhea and vomiting.
There is a need for better understanding of the common and emerging metabolic disorders to combat them effectively. The treatment of metabolic disorders requires an understanding of the underlying cause of the disorder.
Need a Primary Care Physician? Primary Medical Care Center is an Urgent Care Miami provider serving Miami-Dade and Broward County with Two Convenient Locations. Call Now: 305-751-1500 or visit us (11500 NW 7th Ave., Miami, FL 33168, 2412 N State Road 7, Lauderdale Lakes, FL 33313).